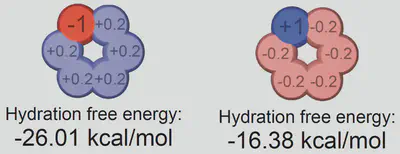
Anion-Cation Contrast in Solute Solvation
Stefan Hervø-Hansen | June 11, 2023 | MSL2023
Drug and materials discovery is a complex, expensive, and time-consuming
Solvation free energies to understand underlying physics of liquid structure
Thermodynamic framework for solvation thermodynamics
$$ \beta \mu^{\mathrm{ex}} = \mu_{\mathrm{r}} + \langle \Delta U_{\mathrm{a}} \rangle_{\lambda=1} + RT \ln \left\langle e^{\beta \left( \langle U_{\mathrm{a}} \rangle - U_{\mathrm{a}} \right)} \right\rangle_{\lambda=1} $$ Energy-Representation Theory of Solvation allows a straightforward route into such an energetic decomposition: $$ \Delta G_{\mathrm{sol}} = \sum_{\mathrm{species},\ i} \Delta G_{\mathrm{sol}, i} $$ $$ \Delta G_{\mathrm{sol},i}=\int \rho(\epsilon) \epsilon \ \mathrm{d}\epsilon - \int \mathcal{F}(\epsilon) \ \mathrm{d}\epsilon $$Widom, J Chem Phys. 1963; van der Vegt & Nayar, J Phys Chem B. 2017; Matubayasi, BCSJ. 2019
Acknowledgements



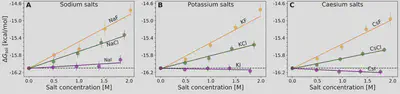
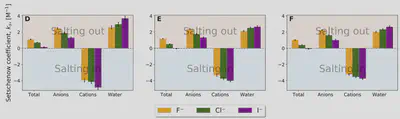
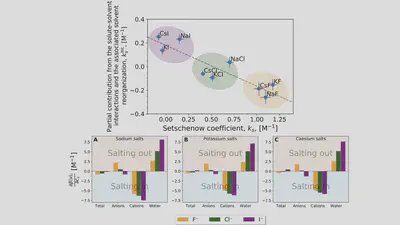
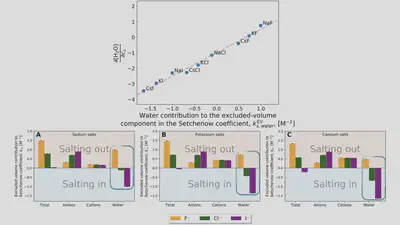
Setschenow coefficients
$$ \ln\left(\frac{S(c_s)}{S(0)}\right) = -k_s c_s = -\frac{\Delta \Delta G_{\mathrm{sol}}}{RT} $$ $$ \Delta \Delta G_{\mathrm{sol}}=\Delta G_{\mathrm{sol}}(c_s)-\Delta G_{\mathrm{sol}}(0) $$Anion-cation contrast
$$ \Delta G_{\mathrm{sol}} = \cancel{\Delta G_{\mathrm{self}}} + \Delta G_{\mathrm{anion}} + \Delta G_{\mathrm{cation}} + \Delta G_{\mathrm{water}} $$ $$ k_s = \frac{1}{RT} \left( \frac{\partial \Delta G_{\mathrm{anion}}}{\partial c_{s}} + \frac{\partial \Delta G_{\mathrm{cation}}}{\partial c_{s}} + \frac{\partial \Delta G_{\mathrm{water}}}{\partial c_{s}} \right) $$Interaction-component analysis
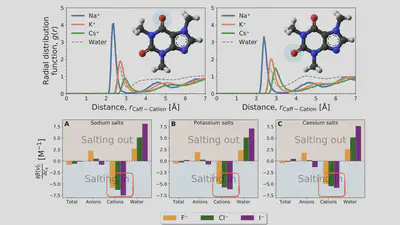
\[\begin{aligned} \mu^{\mathrm{ex}} = & \int_{-\infty}^{\epsilon_{\mathrm{max}}} \varepsilon \rho_1(\varepsilon) \ \mathrm{d}\varepsilon + \int_{-\infty}^{\epsilon_{\mathrm{max}}} \mathcal{F}(\rho_0, \rho_1;\varepsilon) \ \mathrm{d}\varepsilon \\ & +\int_{\epsilon_{\mathrm{max}}}^{\infty} \mathcal{F}(\rho_0, \rho_1;\varepsilon) \ \mathrm{d}\varepsilon \end{aligned} \]Interaction-component analysis: The interaction component
Cation contribution: Binding
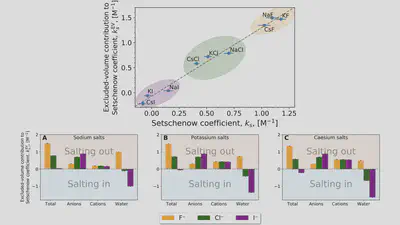
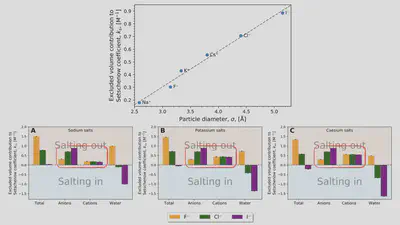
Interaction-component analysis: The excluded-volume component
Interaction-component analysis: The excluded-volume ion component
Interaction-component analysis: The excluded-volume water component
Conclusions
- Free-energy calculations reveal ions can be highly different in their perturbation mechanism.
- Effects not found at full coupling between the solute and solvent (like cavitation) correlates with the Setschenow coefficient.