 Image credit: J. Phys. Chem. B
Image credit: J. Phys. Chem. BAbstract
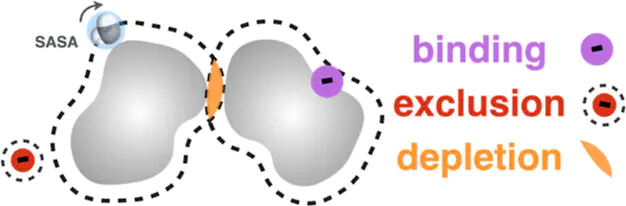
Salts affect the solvation thermodynamics of molecules of all sizes; the Hofmeister series is a prime example in which different ions lead to salting-in or salting-out of aqueous proteins. Early work of Tanford led to the discovery that the solvation of molecular surface motifs is proportional to the solvent accessible surface area (SASA), and later studies have shown that the proportionality constant varies with the salt concentration and type. Using multiscale computer simulations combined with vapor-pressure osmometry on caffeine-salt solutions, we reveal that this SASA description captures a rich set of molecular driving forces in tertiary solutions at changing solute and osmolyte concentrations. Central to the theoretical work is a new potential energy function that depends on the instantaneous surface area, salt type, and concentration. Used in, e.g., Monte Carlo simulations, this allows for a highly efficient exploration of many-body interactions and the resulting thermodynamics at elevated solute and salt concentrations.